The Lifecycle of Low Voltage GCK Switchgear: From Design to Decommission
Release time:
2025-05-12
The Lifecycle of Low Voltage GCK Switchgear: From Design to Decommission
Table of Contents
- 1. Introduction to Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
- 2. The Design Phase of Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
- 3. The Manufacturing Process of GCK Switchgear
- 4. Installation and Commissioning of GCK Switchgear
- 5. Operation and Maintenance of GCK Switchgear
- 6. Upgrades and Modifications Throughout Its Lifecycle
- 7. Decommissioning and Disposal of GCK Switchgear
- 8. Conclusion
- 9. FAQs about Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
1. Introduction to Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
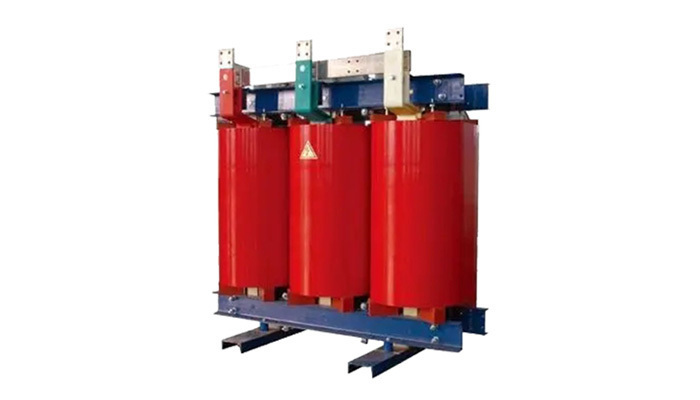
In the realm of electrical engineering, **Low Voltage GCK Switchgear** represents a crucial component in electrical distribution systems. Designed to manage power distribution, it ensures the safety, efficiency, and reliability of electrical operations in various industrial applications. The GCK (General Control Cabinet) switchgear operates at low voltage levels and is essential for controlling and protecting electrical circuits. Understanding its lifecycle—from design to decommission—is vital for professionals in the construction and decorative materials industry.
The lifecycle of GCK switchgear encompasses numerous stages, each contributing to the overall performance and sustainability of the product. Each phase is intricately linked, and missteps in one area can impact the subsequent stages, making it imperative to approach the entire lifecycle with diligence and foresight.
2. The Design Phase of Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
The design phase is the cornerstone of the GCK switchgear lifecycle. An effective design must balance functionality, safety, and compliance with industry standards. Engineers must consider various factors, including:
2.1 Defining Requirements and Standards
Before embarking on the design process, it is crucial to establish specific requirements based on the intended application. This includes understanding load capacities, environmental conditions, and safety regulations. Compliance with international and local standards, such as IEC 61439, ensures that the switchgear meets safety and performance criteria.
2.2 Selecting Materials and Components
Choosing the right materials is fundamental to the durability and performance of GCK switchgear. High-quality conductors, insulators, and protective devices are essential for safe operation. Engineers must also consider the thermal management of components to prevent overheating and ensure long-term reliability.
2.3 Electrical and Mechanical Design
The electrical design focuses on the circuit configuration, protection schemes, and control logic. Simultaneously, mechanical design involves the physical layout, housing, and accessibility of components. Advanced software tools like CAD (Computer-Aided Design) are often utilized to visualize the switchgear and ensure optimal design.
3. The Manufacturing Process of GCK Switchgear
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing phase begins, transforming blueprints into tangible products. This phase involves several critical steps:
3.1 Fabrication of Components
Manufacturing begins with the fabrication of individual components. This includes cutting, bending, and assembling metal enclosures, as well as producing circuit breakers and control devices. **Quality control** during fabrication is essential to ensure that each piece meets the required specifications.
3.2 Assembly of Switchgear
After fabrication, the components are assembled into the final switchgear configuration. During assembly, technicians must ensure that all connections are secure and that there is no risk of electrical faults. This phase often includes **pre-testing** to verify functionality before final assembly.
3.3 Final Testing and Quality Assurance
Before leaving the factory, GCK switchgear undergoes rigorous testing procedures to ensure compliance with safety and performance standards. This includes dielectric strength testing, functional testing, and load testing. Quality assurance is paramount, as it guarantees that the switchgear will perform reliably in the field.
4. Installation and Commissioning of GCK Switchgear
Proper installation is crucial for the successful operation of GCK switchgear. This phase involves several key activities:
4.1 Site Preparation
Preparing the installation site is the first step in the commissioning process. This includes ensuring that the site meets electrical codes and standards, providing adequate space for the switchgear, and ensuring that environmental conditions are appropriate for its operation.
4.2 Installation Procedures
The installation process involves positioning the switchgear, securing it in place, and connecting it to power sources and control systems. It is essential that qualified personnel perform these tasks to minimize the risk of errors or accidents.
4.3 Commissioning Tests
Once installed, GCK switchgear must undergo commissioning tests to verify that all systems function as intended. This includes checking electrical connections, control systems, and safety features. The commissioning phase is critical for ensuring that the switchgear operates efficiently and safely.
5. Operation and Maintenance of GCK Switchgear
After installation, the focus shifts to the operation and maintenance of GCK switchgear. Proper maintenance is essential for prolonging the lifecycle and performance of the equipment.
5.1 Routine Inspections
Regular inspections are necessary to identify potential issues before they escalate. This includes checking for signs of wear, overheating, and corrosion. Routine visual inspections help maintain operational reliability and extend the lifespan of the switchgear.
5.2 Preventive Maintenance
Implementing a preventive maintenance schedule ensures that all components are serviced regularly. This may include tightening connections, cleaning components, and replacing worn parts. Preventive maintenance can reduce the risk of unexpected failures and enhance system performance.
5.3 Troubleshooting and Repairs
In the event of a malfunction, quick action is essential to resolve the issue. Troubleshooting procedures must be in place to identify the root cause of any problems. Repairs should be carried out by qualified technicians to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards.
6. Upgrades and Modifications Throughout Its Lifecycle
As technology advances and operational needs change, GCK switchgear may require upgrades or modifications.
6.1 Technological Advancements
Upgrading components to enhance performance, such as integrating smart technology for monitoring and control, can significantly improve operational efficiency. Upgrading to newer technology helps maintain competitiveness and adapt to industry changes.
6.2 Adapting to New Regulations
As regulations evolve, it may be necessary to modify switchgear to remain compliant. Staying informed about regulatory changes ensures that the switchgear continues to operate safely and legally.
6.3 Capacity Expansion
As businesses grow, the demand for power may increase. Modifications to switchgear may be necessary to accommodate additional load requirements. This can involve adding new circuits or upgrading existing ones to handle increased demand.
7. Decommissioning and Disposal of GCK Switchgear
The final phase in the lifecycle of GCK switchgear is decommissioning. This phase must be managed carefully to minimize environmental impact and ensure safety.
7.1 Planning for Decommissioning
In preparation for decommissioning, a detailed plan should be developed. This plan includes evaluating the condition of the switchgear, determining the best disposal methods, and complying with environmental regulations.
7.2 Safe Removal and Disposal
The removal process must be conducted safely, ensuring that all electrical connections are properly disconnected. Disposal of components must be handled according to local regulations, with an emphasis on recycling materials whenever possible to reduce waste.
7.3 Documentation and Reporting
Finally, thorough documentation of the decommissioning process is essential. This includes keeping records of the removal, disposal methods, and any recycled materials. Proper reporting ensures compliance with regulatory requirements and aids in future evaluations.
8. Conclusion
The lifecycle of Low Voltage GCK Switchgear encompasses critical phases that highlight the importance of careful planning, design, manufacturing, installation, operation, maintenance, upgrades, and decommissioning. Each stage plays a vital role in ensuring that the switchgear operates efficiently and safely throughout its lifespan. Understanding this lifecycle is crucial for professionals in the construction and decorative materials industry, enabling informed decisions that enhance system performance and sustainability.
9. FAQs about Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
What is Low Voltage GCK Switchgear?
Low Voltage GCK Switchgear is a type of electrical switchgear used to control and protect electrical circuits at low voltage levels. It is essential for effective power distribution in industrial applications.
What are the key components of GCK Switchgear?
Key components include circuit breakers, control devices, busbars, and protective relays, all housed within a durable enclosure designed for safety and efficiency.
How often should GCK Switchgear be maintained?
Routine inspections should be conducted regularly, at least once every six months, while preventive maintenance schedules can vary based on operational demands and environmental conditions.
What are the benefits of upgrading GCK Switchgear?
Upgrading GCK Switchgear can improve operational efficiency, enhance safety, and ensure compliance with the latest regulations and technological advancements.
How is GCK Switchgear decommissioned?
Decommissioning involves careful planning, safe removal of components, and responsible disposal methods, including recycling when possible, to minimize environmental impact.
By following the detailed process outlined above, stakeholders can ensure that their Low Voltage GCK Switchgear operates effectively, supports safety, and adheres to industry standards throughout its entire lifecycle.
Latest information
Get a Free Consultancy
If you have any suggestions, please leave a message or send an email to us.