How to Conduct a Risk Assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear: Essential Guidelines for Safety and Compliance
Release time:
2025-04-12
How to Conduct a Risk Assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
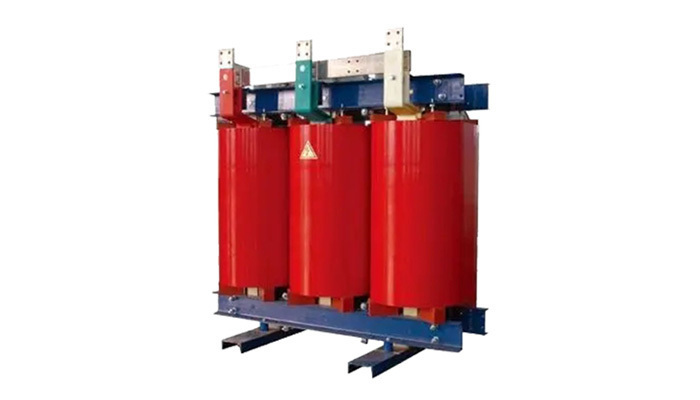
Introduction to Low Voltage GCK Switchgear
Low Voltage GCK Switchgear is critical in managing electrical systems within various industries, including construction and manufacturing. Understanding how to conduct a risk assessment for this equipment is vital for ensuring safety, compliance, and operational efficiency. A systematic approach to risk assessment not only enhances workplace safety but also minimizes potential liabilities associated with electrical failures.
Understanding Risk Assessment in Electrical Systems
Risk assessment involves identifying hazards, analyzing and evaluating the risks associated with those hazards, and determining appropriate control measures. In the context of low voltage GCK switchgear, it is crucial to assess risks to protect personnel, equipment, and the integrity of operations.
The Importance of Risk Assessment for GCK Switchgear
Conducting a thorough risk assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear is essential for several reasons:
- **Safety of Personnel**: Protecting workers from electrical hazards is paramount.
- **Compliance with Regulations**: Adhering to safety standards and legal requirements helps avoid penalties.
- **Operational Efficiency**: Minimizing downtime related to electrical failures enhances productivity.
- **Asset Protection**: Safeguarding equipment from damage due to electrical faults prolongs lifespan and reduces replacement costs.
Key Steps in Conducting a Risk Assessment for GCK Switchgear
Undertaking a risk assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear involves several critical steps.
1. Identify Potential Hazards
Begin by identifying all potential hazards associated with the switchgear. This includes:
- **Electrical Shock Risks**: Assessing exposure to live parts and faulty equipment.
- **Arc Flash Hazards**: Evaluating areas where electrical discharges could occur.
- **Thermal Risks**: Monitoring for overheating components that could lead to fire hazards.
- **Mechanical Risks**: Identifying moving parts that could present physical hazards.
2. Evaluate Risks Associated with Each Hazard
Once hazards are identified, evaluate the risks they pose. Consider factors such as:
- **Likelihood of Occurrence**: How often might the hazard lead to an incident?
- **Severity of Impact**: What would be the potential consequences if an incident occurs?
- **Existing Control Measures**: Assess the effectiveness of current safety systems and protocols in place.
3. Determine Risk Levels
Utilize a risk matrix to categorize risks based on their likelihood and severity. This classification will help prioritize which risks require immediate attention and further control measures.
Risk Rating Scale Example
- **Low Risk (1-3)**: Acceptable risk; routine monitoring is sufficient.
- **Medium Risk (4-6)**: Action required; implement additional control measures.
- **High Risk (7-9)**: Immediate action required; address risks to prevent incidents.
4. Implement Control Measures
For each identified risk, develop and implement appropriate control measures. These may include:
- **Engineering Controls**: Implementing safety barriers or redesigning equipment to reduce exposure.
- **Administrative Controls**: Establishing safety protocols, training programs, and clear operational procedures.
- **Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)**: Ensuring workers have access to and are trained in using necessary PPE.
5. Monitor and Review the Risk Assessment
Risk assessments are not one-time activities; they should be regularly reviewed and updated. Changes in operational processes, equipment, or regulations may necessitate adjustments to the risk assessment.
Essential Tools for Risk Assessment
Utilizing the right tools can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your risk assessment process.
1. Hazard Identification Checklists
Create comprehensive checklists to ensure all potential hazards are examined during the risk assessment.
2. Risk Assessment Software
Consider using digital tools designed for risk assessment, which can help streamline the process and provide reports.
3. Training and Resources
Provide ongoing training for personnel involved in the risk assessment process to ensure they are up-to-date with the latest safety practices and technologies.
Best Practices for Conducting Risk Assessments on GCK Switchgear
To ensure a comprehensive and effective risk assessment, adhere to the following best practices:
1. Engage Stakeholders
Involve key stakeholders, including maintenance personnel, safety professionals, and operational staff, in the risk assessment process. Their insights can provide valuable perspectives on potential hazards.
2. Document All Findings
Maintain meticulous records of the risk assessment process, including identified hazards, evaluations, control measures, and reviews. This documentation serves as a reference and a compliance record.
3. Continuous Improvement
Adopt a culture of continuous improvement by regularly revisiting risk assessments and updating practices based on new technologies and industry standards.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance in Risk Assessment
Understanding and adhering to relevant regulations is crucial for conducting a compliant risk assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear.
1. International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) Standards
Familiarize yourself with IEC standards related to low voltage switchgear to ensure compliance with international safety protocols.
2. National Electrical Code (NEC)
In the United States, ensure your risk assessment aligns with the NEC requirements, which govern electrical installations and safety.
3. Local Regulations
Always consider local regulations and standards that may affect electrical installations and safety measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Low Voltage GCK Switchgear?
Low Voltage GCK Switchgear is a type of electrical equipment used for controlling, distributing, and protecting electrical power in low voltage networks.
2. Why is a risk assessment necessary for switchgear?
Risk assessments help identify potential hazards, evaluate risks, and implement measures to ensure safety and compliance in electrical installations.
3. How often should risk assessments be conducted?
Risk assessments should be conducted regularly and updated whenever there are changes in the operational environment or equipment.
4. What are common hazards associated with GCK Switchgear?
Common hazards include electrical shocks, arc flash incidents, overheating, and mechanical risks from moving parts.
5. How can I improve safety in my electrical operations?
Improving safety can be achieved by regularly conducting risk assessments, providing adequate training, and implementing effective safety measures.
Conclusion
Conducting a thorough risk assessment for Low Voltage GCK Switchgear is essential for maintaining safety, compliance, and operational effectiveness. By following the outlined steps, utilizing appropriate tools, and adhering to best practices, organizations can significantly reduce the risks associated with electrical systems. Continual monitoring and improvement of risk management practices will ensure that safety remains a priority in all operations involving low voltage switchgear. Prioritizing safety not only protects personnel and equipment but also fosters a culture of responsibility and diligence within the organization.
Latest information
Get a Free Consultancy
If you have any suggestions, please leave a message or send an email to us.